Parboiling of paddy involves a hydrothermal treatment where rice is processed through soaking, heating, steaming, and drying before milling. This partially cooks the rice, transforming its starch and transferring natural vitamins and minerals from the bran to the grain. Water and steam are essential in converting the raw cereals into parboiled rice.
Paddy is immersed in large water-filled vessels at specific temperatures for different rice varieties. Careful monitoring during soaking is essential as it varies with each rice type and prevailing weather conditions. This process enhances the vitamin B content and reduces the percentage of broken grains. It also improves the hardness of parboiled rice, helping it retain its shape even after cooking.
Steaming alters the physical structure of rice while preserving its nutrients, increasing production yield, and facilitating storage and drying. It enhances grain length and ensures uniform colour in parboiled rice. Pre-steaming softens the paddy, reducing soaking time and increasing the rice’s capacity to absorb water during cooking.
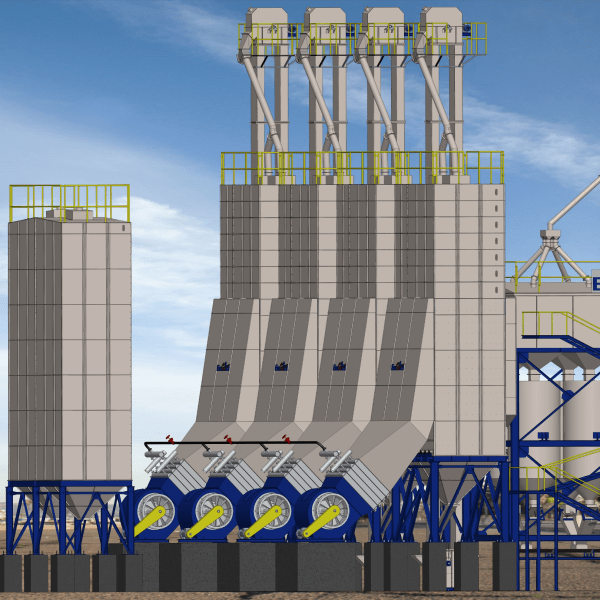
100-120 TPD Complete Rice Parboiling and Milling Plant
Capacity: 100-120 tons/day
Parboiled rice milling involves using steamed rice as the primary material. The process includes cleaning, soaking, cooking, drying, and cooling, followed by conventional rice processing methods to produce the final rice product. The finished parboiled rice fully absorbs the nutrients and has an excellent flavour. The boiling process also eradicates pests, making the rice easier to store.
Paddy parboiling is a hydrothermal process where the starch granules within the rice grain are gelatinized using steam and hot water. The milling of parboiled rice involves using steamed rice as raw material, followed by cleaning, soaking, cooking, drying, and cooling after heat treatment. This process enhances the nutritional content and flavour of the rice, while also making it easier to store due to the pest elimination during boiling.
We supply fully automated, modern parboiled rice milling plants with various production capabilities to meet your demands. The complete plant consists of two main sections: the rice parboiling section and the rice milling section.
- Paddy Cleaning: This stage removes impurities from the paddy, such as straw, stones, and dust. Clean paddy ensures better water quality during soaking and prevents damage to downstream processing equipment, making it a crucial step in the parboiling process.
- Paddy Soaking: The goal is to ensure the paddy absorbs enough water to facilitate starch gelatinization. The rice must absorb over 30% water for effective steaming. Using vacuuming, constant temperature, and pressure soaking methods, the rice quickly absorbs water to reach the necessary moisture level. Soaking temperature ranges from 55-70 degrees Celsius for 3.5-4.5 hours, depending on the rice variety and quality
- Steaming and Boiling: After soaking, the paddy is steamed to achieve starch gelatinization. High-pressure and high-temperature steam must be controlled to ensure uniformity. Proper steaming results in transparent honey-coloured parboiled rice. The cooking parameters can be adjusted to produce rice with varying colour shades as per customer requirements.
- Parboiled Paddy Drying: This step reduces the moisture content from around 35% to approximately 14%, facilitating storage and transport while maximising production yield. The drying process uses boiler heat converted into air via a heat exchanger, ensuring the rice remains uncontaminated and odour-free. Drying is done in two stages: rapid drying to reduce moisture content to 20%, followed by slow drying to minimise waist burst rate and improve whole grain yield.
- Parboiled Paddy Cooling: The dried paddy is temporarily stored in vertical silos equipped with ventilation fans to remove residual heat and ensure even moisture distribution before processing.
- Rice Husking and Separation: The husk is removed using a hulling machine. The paddy separator then separates brown rice from paddy based on specific gravity and friction coefficient differences.
- Rice Milling: Pearling of parboiled rice requires more time than normal paddy due to its smectic nature post-soaking. To address this, a blower rice miller with increased rotating speed and pneumatic bran transmission is used, reducing friction and maintaining rice quality.
- Rice Polishing: This process involves spraying water to polish the rice surface, forming a smooth gelatinous layer that extends preservation time. Extended polishing produces high-quality, glossy rice, enhancing its appearance and value.
- Rice Grading: The grading machine efficiently sieves milled rice into different categories: head rice, large broken, medium broken, and small broken.
- Rice Color Sorting: The colour sorting machine removes defective rice and impurities, ensuring high-quality output. It uses CCD signals to detect and eject unqualified rice or impurities.
- Finished Rice Packing: The final rice product is weighed and packed using an automatic packing machine, which can handle bags ranging from 1 to 50 kg. This machine is electric and programmable, facilitating efficient packing for supply to customers.
The output selection for the paddy parboiling plant depends on the subsequent rice milling machine's capacity and power. Adequate parboiled rice must be available before hulling to ensure smooth operation. If necessary, two units can be connected in parallel to meet output requirements.
As pioneers in the industry, we manufacture an impeccable range of Paddy Parboiling Plants, offering complete plants, installation services, and training. If interested in this project, please feel free to contact us for further information.
Features of Our Rice Parboiling and Milling Plant:
- Built from prime, tested materials for durability and consistent quality.
- Uniform steaming with a steam distribution system ensures even cooking and drying.
- Two overhead water tanks for easy cold water lifting.
- Increased plant height ensures better flow and reduces spillage.
- Uniform drying with thick baffles for slow, steady drying, minimising grain breakage.
- Factory-assembled, fully bolted and foldable construction, with 90% of materials manufactured in-house for quick installation.
- Low energy consumption due to efficient blower and elevator design.
- Minimal labour required due to automated operations.
Main Flow Chart:
Cleaning →Soaking →Steaming →Drying →Husking →Polishing and Grading →Color Sorting →Packing
Single/Double Boiled Rice Production
This plant is designed to produce two types of parboiled rice: Half Parboiled Rice (Single Steaming Process) and Full Parboiled Rice (Double Steaming Process).
Half Parboiled Rice (Single Steaming Process)
Some parboiled rice consumers prefer rice with a translucent kernel and an opaque (dull white) centre and sides. This type of rice cooks quickly and has a soft texture.
The process involves soaking raw paddy in circulated water at room temperature for 12 hours, depending on atmospheric conditions and the desired extent of the white core. The soaked paddy is then thoroughly drained and transferred to a cooker for final steaming. After steaming, the paddy is sent to a dryer for uniform drying, reducing the moisture content to the 11-12% range. The processed paddy is then transferred to tempering bins or silos for stabilisation.
Paddy parboiling is a hydrothermal process where the starch granules within the rice grain are gelatinized using steam and hot water. The milling of parboiled rice involves using steamed rice as raw material, followed by cleaning, soaking, cooking, drying, and cooling after heat treatment. This process enhances the nutritional content and flavour of the rice, while also making it easier to store due to the pest elimination during boiling.
We supply fully automated, modern parboiled rice milling plants with various production capabilities to meet your demands. The complete plant consists of two main sections: the rice parboiling section and the rice milling section.